Lupine Publishers|chemistry journals
In the current editorial, we study Palau’amine and Olympiadane
Nano molecules (Figures 1 & 2) incorporation into the Nano
Polymeric Matrix (NPM) by immersion of the Nano Polymeric
Modified Electrode (NPME) as molecular enzymes and drug
targets for human cancer cells, tissues and tumors treatment
under synchrotron and synchrocyclotron radiations. In this regard,
the development of Chemical Modified Electrodes (CEMs) is at
present an area of great interest. CEMs can be divided broadly into
two main categories; namely, surface modified and bulk modified
electrodes. Methods of surface modification include adsorption,
covalent bonding, attachment of polymer Nano films, etc. Polymer
Nano film coated electrodes can be differentiated from other
modification methods such as adsorption and covalent bonding
in that they usually involve multilayer as opposed to monolayer
frequently encountered for the latter methods. The thicker Nano
films imply more active sites which lead to larger analytical
signals. This advantage coupled with other, their versatility and
wide applicability, makes polymer Nano film modified electrodes
particularly suitable for analytical applications [1–27].
Editorial
Figure 1: Molecular structure of Palau’amine Nano molecules.
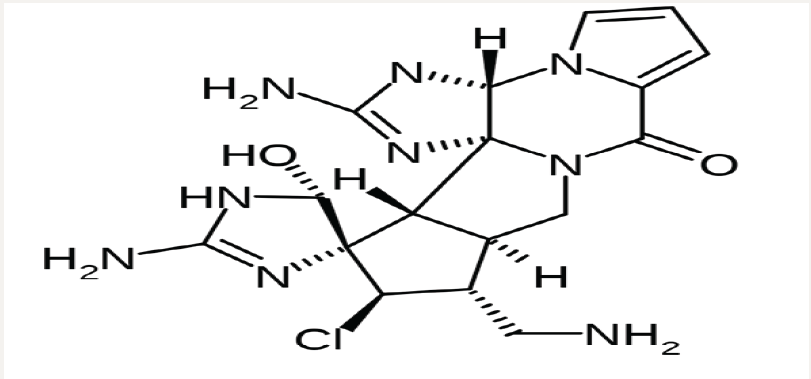

Figure 2: Molecular structure of Olympiadane Nano molecules.
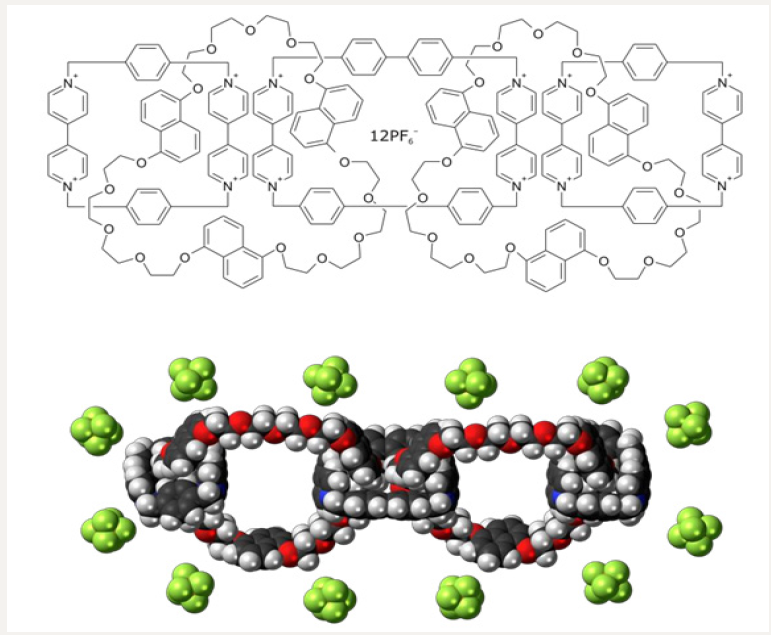
Electrochemical polymerization offers the advantage of
reproducible deposition in terms of Nano film thickness and loading,
making the immobilization procedure of a metal–based electro
catalyst very simple and reliable for Palau’ amine and Olympiadane
Nano molecules–encapsulating Carbon nanotubes incorporation
into the Nano Polymeric Matrix (NPM) by immersion of the Nano
Polymeric Modified Electrode (NPME) as molecular enzymes and
drug targets for human cancer cells, tissues and tumors treatment
under synchrotron and synchrocyclotron radiations. Also, it must
be notice that the nature of working electrode substrate in electro
preparation of polymeric Nano film is very important, because
properties of polymeric Nano films depend on the working electrode
anti–cancer Nano materials. The ease and fast preparation and of
obtaining a new reproducible surface, the low residual current,
porous surface and low cost of Multi–Walled Carbon Nanotubes
(MWCNTs) paste are some advantages of Carbon Paste Electrode
(CPE) over all other solid electrodes [28–92].
On the other hand, it has been shown that, macrocyclic complexes of Palau’amine and Olympiadane Nano molecules– encapsulating Carbon nanotubes are interest as modifying agents because in basic media Palau’amine and Olympiadane Nano molecules–encapsulating Carbon nanotubes redox centers show high catalytic activity towards the oxidation of small organic anti-cancer Nano compounds. The high–valence species of Palau’amine and Olympiadane Nano molecules–encapsulating Carbon nanotubes seem to act as strong oxidizing agents for low-electroactivity organic substrates. 1,2–Dioxetane (1,2– Dioxacyclobutane), 1,3–Dioxetane (1,3– Dioxacyclobutane), DMDM Hydantoin and Sulphobe as the anti–cancer organic intermediate products of methanol oxidation as well as formic acid, is important to investigate its electrochemical oxidation behavior in Palau’ amine and Olympiadane Nano molecules-encapsulating Carbon nanotubes incorporation into the Nano Polymeric Matrix (NPM) by immersion of the Nano Polymeric Modified Electrode (NPME) as molecular enzymes and drug targets for human cancer cells, tissues and tumors treatment under synchrotron and synchrocyclotron radiations [93–110].
In this editorial, we decided to combine the above mentioned advantageous features for the aim of Palau’ amine and Olympiadane Nano molecules–encapsulating Carbon nanotubes incorporation into the Nano Polymeric Matrix (NPM) by immersion of the Nano Polymeric Modified Electrode (NPME) as molecular enzymes and drug targets for human cancer cells, tissues and tumors treatment under synchrotron and synchrocyclotron radiations. Furthermore, in this editorial, we prepared poly Nano films by electropolymerization at the surface of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes (MWCNTs) paste electrode. Then, Palau’amine and Olympiadane Nano molecules–encapsulating Carbon nanotubes were incorporated into the Nano Polymeric Matrix (NPM) by immersion of the Nano Polymeric Modified Electrode (NPME) in a solution. The modifier layer of Palau’amine and Olympiadane Nano molecules–encapsulating Carbon nanotubes at the electrode surface acts as a Nano catalyst for the treatment of human cancer cells, tissues and tumors under synchrotron and synchrocyclotron radiations. Suitability of this Palau’amine and Olympiadane Nano molecules–encapsulating Carbon nanotubes–modified polymeric Multi–Walled Carbon Nano tubes (MWCNTs) paste electrode toward the electrocatalytic treatment of human cancer cells, tissues and tumors under synchrotron and synchrocyclotron radiations in alkaline medium at ambient temperature was investigated [111– 153].

On the other hand, it has been shown that, macrocyclic complexes of Palau’amine and Olympiadane Nano molecules– encapsulating Carbon nanotubes are interest as modifying agents because in basic media Palau’amine and Olympiadane Nano molecules–encapsulating Carbon nanotubes redox centers show high catalytic activity towards the oxidation of small organic anti-cancer Nano compounds. The high–valence species of Palau’amine and Olympiadane Nano molecules–encapsulating Carbon nanotubes seem to act as strong oxidizing agents for low-electroactivity organic substrates. 1,2–Dioxetane (1,2– Dioxacyclobutane), 1,3–Dioxetane (1,3– Dioxacyclobutane), DMDM Hydantoin and Sulphobe as the anti–cancer organic intermediate products of methanol oxidation as well as formic acid, is important to investigate its electrochemical oxidation behavior in Palau’ amine and Olympiadane Nano molecules-encapsulating Carbon nanotubes incorporation into the Nano Polymeric Matrix (NPM) by immersion of the Nano Polymeric Modified Electrode (NPME) as molecular enzymes and drug targets for human cancer cells, tissues and tumors treatment under synchrotron and synchrocyclotron radiations [93–110].
In this editorial, we decided to combine the above mentioned advantageous features for the aim of Palau’ amine and Olympiadane Nano molecules–encapsulating Carbon nanotubes incorporation into the Nano Polymeric Matrix (NPM) by immersion of the Nano Polymeric Modified Electrode (NPME) as molecular enzymes and drug targets for human cancer cells, tissues and tumors treatment under synchrotron and synchrocyclotron radiations. Furthermore, in this editorial, we prepared poly Nano films by electropolymerization at the surface of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes (MWCNTs) paste electrode. Then, Palau’amine and Olympiadane Nano molecules–encapsulating Carbon nanotubes were incorporated into the Nano Polymeric Matrix (NPM) by immersion of the Nano Polymeric Modified Electrode (NPME) in a solution. The modifier layer of Palau’amine and Olympiadane Nano molecules–encapsulating Carbon nanotubes at the electrode surface acts as a Nano catalyst for the treatment of human cancer cells, tissues and tumors under synchrotron and synchrocyclotron radiations. Suitability of this Palau’amine and Olympiadane Nano molecules–encapsulating Carbon nanotubes–modified polymeric Multi–Walled Carbon Nano tubes (MWCNTs) paste electrode toward the electrocatalytic treatment of human cancer cells, tissues and tumors under synchrotron and synchrocyclotron radiations in alkaline medium at ambient temperature was investigated [111– 153].
For more Lupine
Publishers Open Access Journals Please visit our website:
http://lupinepublishers.us/
For more Open Access Journal on Chemistry articles Please Click Here:
https://lupinepublishers.com/chemistry-journal/
http://lupinepublishers.us/
For more Open Access Journal on Chemistry articles Please Click Here:
https://lupinepublishers.com/chemistry-journal/




